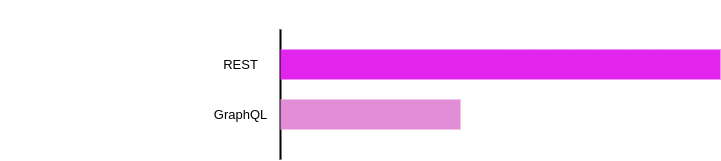GraphQL vs REST? Understanding the Strengths and Trade-offs
What is GraphQL?
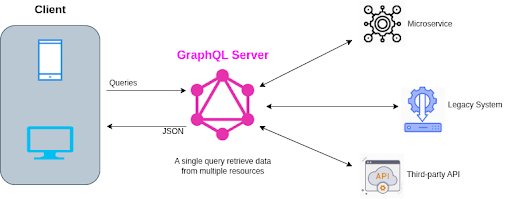
GraphQL is a query language for APIs and a runtime for fulfilling those queries with your existing data. GraphQL provides a complete and understandable description of the data in your API, gives clients the power to ask for exactly what they need and nothing more, makes it easier to evolve APIs over time, and enables powerful developer tools.
Key Advantages
GraphQL was created to address some of the limitations of REST APIs, particularly issues like over-fetching. It offers an efficient and flexible way to request and manipulate data. Key advantages of GraphQL include:
- Unified Endpoint: Instead of multiple API routes, GraphQL consolidates all operations into a single endpoint, simplifying API structure and reducing the complexity of managing multiple URLs.
- Precise Data Fetching: Clients can request only the specific data they need, minimizing over-fetching and under-fetching. This enhances network efficiency by transmitting only relevant data objects.
- Defined Data Structure: GraphQL enforces a schema that defines data types and their relationships, providing a structured and clear representation of available data.
- Built-in Introspection: GraphQL APIs are self-documenting, allowing clients to query the schema to explore available types, queries, mutations, and fields. This makes it easier to understand and interact with the API.
- Fewer Network Calls: In REST, retrieving related data often requires multiple endpoint requests. GraphQL enables clients to fetch data from multiple related resources in a single query, significantly reducing the number of network calls and improving application performance.
What is REST?
REST, short for Representational State Transfer, is an architectural approach that enables seamless communication between a client and a server through a standardized interface. It defines specific operations that leverage standard HTTP methods to execute CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) actions on resources.
Advantages of Using REST APIs
REST APIs offer several advantages that simplify development and enable the creation of efficient, scalable systems. Key benefits include:
- Ease of Adoption: Developers familiar with HTTP can quickly grasp REST, as it follows standard HTTP methods and conventions, making it intuitive to use.
- Language Independence: REST APIs can be built using any programming language that supports HTTP, without requiring additional communication layers or dependencies.
- Extensive Community and Tooling: With over three decades of widespread adoption, REST benefits from a strong developer community and a rich ecosystem of tools that enhance API development and integration.
- Consistent Interface: REST’s uniform architecture ensures a standardized and predictable interaction model, simplifying system integration and communication.
How GraphQL and REST Work
Let’s imagine we’re building a blog application, and the frontend needs to display:
- A user’s name
- Their email address
- Their latest 3 published posts (with title and date)
Example: GraphQL Query
query {
user(id: “123”) {
name
posts(limit: 3) {
title
publishedAt
}
}
}
Response:
{
“data”: {
“user”: {
“name”: “XYZ”,
“email”: “xyz@example.com”,
“posts”: [
{
“title”: “Understanding Async in JS”,
“publishedAt”: “2024-11-01”
},
{
“title”: “REST vs GraphQL”,
“publishedAt”: “2024-10-15”
},
{
“title”: “How to Use Git Like a Pro”,
“publishedAt”: “2024-10-01”
}
]
}
}
}
🔍 Analysis:
- One request to a single /graphql endpoint.
- Only the required fields are returned.
How REST Works
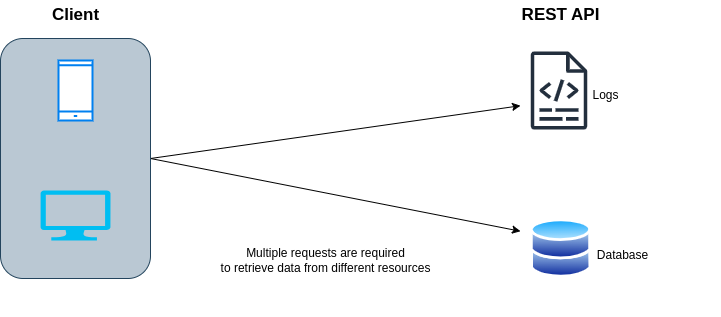
In a RESTful API, data is structured around resources, each accessible via its own URL (endpoint). To retrieve user and post data, multiple HTTP requests are often required.
Example: REST API Calls
GET /users/123
Response:
{
“id”: 123,
“name”: “XYZ”,
“email”: “xyz@example.com”,
“age”: 28
}
To get the user’s posts:
GET /users/123/posts?limit=3
Response:
[
{
“id”: 1,
“title”: “Understanding Async in JS”,
“publishedAt”: “2024-11-01”
},
{
“id”: 2,
“title”: “REST vs GraphQL”,
“publishedAt”: “2024-10-15”
},
{
“id”: 3,
“title”: “How to Use Git Like a Pro”,
“publishedAt”: “2024-10-01”
}
]
🔍 Analysis:
- Requires two network calls.
- The response may include more data than necessary (like age).
Main Differences Between GraphQL and REST
GraphQL and REST differ in their design principles and data modeling approaches. Some key distinctions include:
-
Schema Enforcement
- GraphQL: Mandates the use of a schema, whether developers follow a schema-first or code-first approach. In a code-first approach, the schema is derived from resolvers.
- REST: Does not inherently require a schema. While developers can adopt a schema-first approach using specifications like OpenAPI or generate schemas from code, this is not a core requirement of REST architecture.
-
HTTP Status Codes
- GraphQL: Always returns a 200 status code, even for errors. Instead of relying on HTTP status codes, error details are included within the response payload.
- REST: Utilizes standard HTTP status codes to indicate the outcome of a request, making error handling more straightforward and consistent with traditional web protocols.
-
Versioning
- GraphQL: Uses a single versioned endpoint and manages changes by evolving the schema. Deprecations are handled within the schema itself, eliminating the need for explicit API versioning and allowing for a seamless transition over time.
- REST: Typically requires versioning to manage changes and deprecations safely. This is often implemented within the API URL, though other versioning strategies can also be used.
-
Performance
- GraphQL: Offers clients greater flexibility by allowing them to request only the exact data they need. This minimizes unnecessary data transfer and reduces the need for multiple requests, improving efficiency.
- REST: Can lead to over-fetching (retrieving more data than required) or under-fetching (not getting enough data in a single request), depending on how the API is designed. In some cases, clients may need to make multiple requests to gather all necessary data.
-
Popularity
- GraphQL: Introduced by Facebook in 2015, GraphQL has seen rapid adoption in recent years. According to the report, 29% of developers currently use GraphQL.
- REST: A long-standing standard for API development, REST has been widely used for decades, particularly for public APIs. 90% of developers rely on REST APIs.
When to use GraphQL?
If a project requires efficient data fetching, real-time updates, and a dynamic frontend, GraphQL may be the better choice.
When to use REST?
If needs a well-established, scalable, and simple API structure with standard HTTP status codes, REST is a solid option.